LiDAR Mapping
LiDAR Mapping
LiDAR Mapping
An acronym for light detection and ranging, LIDAR is a remote sensing method that uses pulsed laser to measure ranges (variable distances) and generate precise, 3D data. The key component of a quality LIDAR system is the laser source transmitting the beam.
Wide-area, Corridor and City Mapping, and Urban Planning
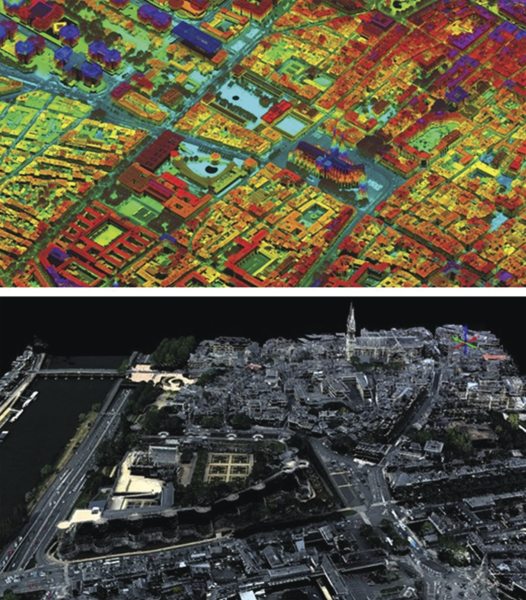

Vegetation Mapping

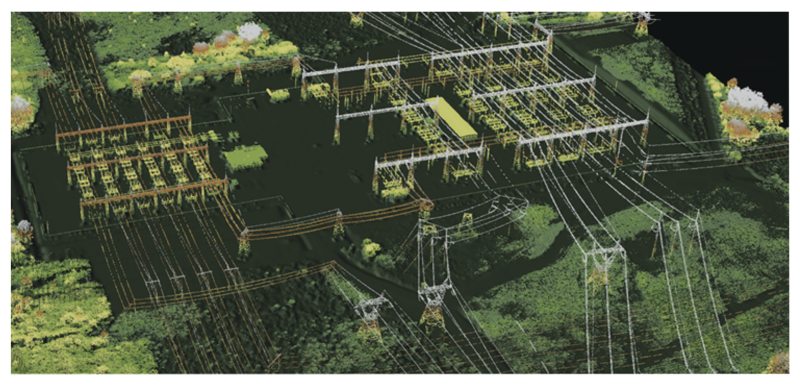
Power Lines
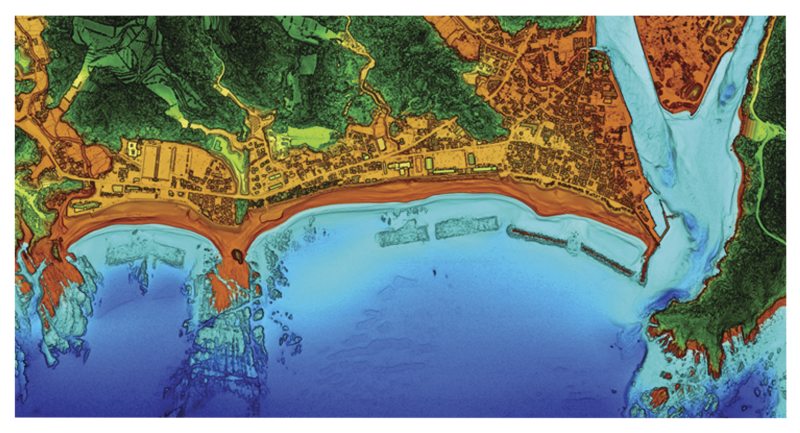
Coastal Mapping
Archaeological and Historical Surveys
The discoveries in the jungles of Central America that were made possible through novel LiDAR 3D terrain mapping tools revealed a huge number of Mayan structures buried deep beneath the jungle of Guatemala's Peten region. In addition to hundreds of previously unknown structures, the LiDAR images show raised highways connecting urban centers and quarries. Complex irrigation and terracing systems supported intensive agriculture capable of feeding masses of workers who dramatically reshaped the landscape. This discovery suggests that this 1200-year-old civilization was more advanced than previously imagined and was comparable to sophisticated cultures such as those in ancient Greece or China.
Future Directions in LiDAR Applications
In addition to higher repetition rates, LiDAR applications will require higher power lasers while maintaining near-diffraction-limited beam quality to achieve higher altitudes and acquisition rates. Furthermore, shorter pulse durations (~1 ns) will be necessary to achieve higher precision. Together with improvements in pulsed fiber lasers, airborne LiDAR will continue to show remarkable advancements resulting in positive changes for various industries, such as increased efficiency in resource management, more effective infrastructure planning, and better preparation for natural disasters.
Related Topics
Optical Components
Remote Sensing